Cells are anatomical and physiological units found in all living beings, which allow their proper functioning and development. These are divided into two types, prokaryotes and eukaryotes, where the former are present in arches and bacteria; while the second in plants, animals, protists and fungi.
Among eukaryotes we find the animal cell, which is defined as that which makes up the tissues present in animals. Of which we will mention some data of interest such as its structure or parts, the functioning of each one of them and the difference with other eukaryotic cells.
With regard to the functioning of animal cells in general, these, like other cells, fulfill the objective of helping in the correct functioning of processes essential for the existence of animals; for example, they intervene in the creation of fabrics, identify sensations, among others.
What is the structure or parts of the animal cell?
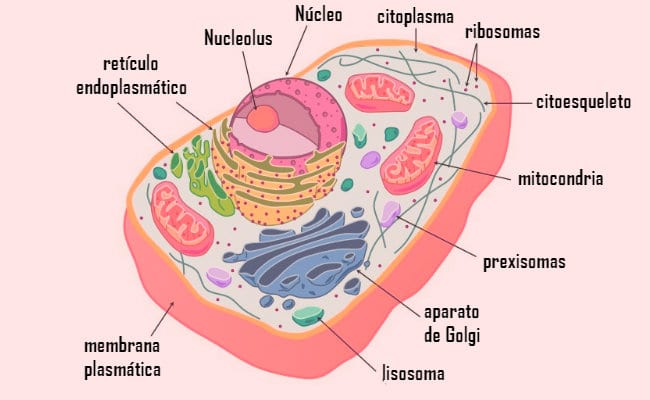
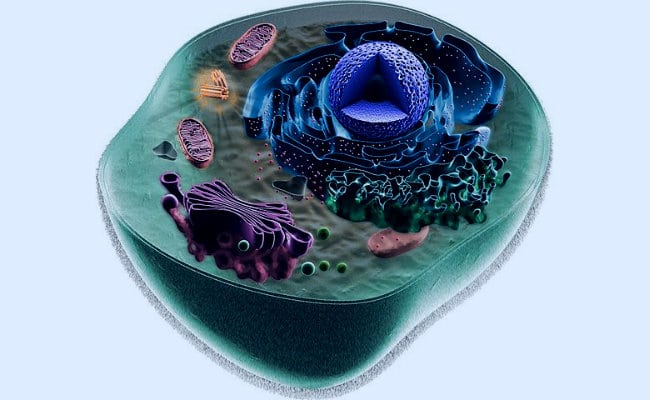
There are trillions of these cells in animals and humans, where each has a structure that comprises the cell envelope, cytoplasm and cell nucleus. In turn, within them it is possible to find the parts of the cell and that each one fulfills a specific function.
The cell or plasma membrane
Located in the cell envelope, it defines as the outer part of the cells, which delimits them and, in turn, functions as a protection and control system of what may or may not come out of them.
Cytoplasm
For its part, the cytoplasm is located between the nucleus of animal cell and the aforementioned membrane; which has a large number of organelles that meet different objectives. It is composed of two parts, an external one (near the membrane) and an internal one (near the nucleus) and, in turn, contains a network of membranes that are beneficial for the biochemical processes that take place in it.
The purpose of this part of the cell is only to house said organelles and to help in their proper development. Among them it is possible to find the reticle smooth and rough endoplasmic cells, centrioles, ribosomes, lysosomes, mitochondria, and the golgi apparatus.
Smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum.
The endoplasmic reticulum is defined as a membrane set that form an interconnected system, which are located in different parts of the animal cell according to the functions to be performed. This can be divided into two, the smooth and the rough or endocrine.
- The smooth refers to the one whose objective is to synthesize the vast majority of lipids found in the cell membrane and those that comprise the other structures. In addition, it is also part of the process of releasing or absorbing the case as needed.
- For its part, the rough is responsible for manufacturing proteins ready to be transported to other parts of the cell, where some of them, such as the Golgi apparatus, can serve as a means to send them outside the cell.
Centrioles
Within the cytoskeleton it is possible to find the centrioles, which are organelles that carry out the function of transporting particles or other organelles in the cell, intervene in the process of cell division, they maintain the shape of the cell and many other functions.
- Centrosome: The centrioles are in charge of joining together to form the "diplosomes" between two of them, which, being together with the pericentriolar material, becomes the centrosome, which is in charge of organizing the microtubules.
- Ribosomes: Ribosomes are present in various parts of the animal cell, such as the endoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria. These fulfill the function of translators, which synthesize the proteins from the information received from the messenger RNA.
Lysosomes
These are usually found in cells that meet the objective of dealing with diseases; since it contains digestive hydrolytic enzymes, which allow the degradation of more complex molecules. Furthermore, it is only present in eukaryotic cells.
Mitochondria
Considering the engine that allows the cell to function, since it converts the nutrients into fuel for the cells; which is made up of ATP, which is the energy of adenosine triphosphate.
The Golgi apparatus
It is that system of membranes that is found within the cell in order to distribute and modify the proteins that are synthesized in the rough or endocrine reticulum.
The cell nucleus
The organelle is called the cell nucleus located in the center of animal cells and it is formed by the nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, chromatin and nucleolus.
- Membrane or nuclear envelope: It consists of the structure that protects or delimits the nucleus from the other parts that make up the animal cell, which is divided into two parts: the internal and the external part. Its function is to provide the space necessary for the transcription of DNA into RNA and, in turn, allow the information from RNA to be translated into protein.
- Nucleoplasm: Also known as cariplasma or nuclear cytosolIt is the "semi-liquid" found in the internal part of the cell nucleus; where chromatin and nucleoli are found. This is intended to allow the chemical reactions that take place in the nucleus.
- Chromatin: Chromatin is the name given to the substance that includes those elements that make up the genome, that is, the poteins, DNA and RNA of eukaryotic chromosomes.
- Nucleolus: The nucleolus is a non-membrane structure that aims at transcription of RNA and the formation of ribosomes; For this, processes such as the synthesis of ARENr or the assembly of proteins intervene. On the other hand, it also fulfills functions such as regulating the cycle of cells, directing their stress responses and also intervening in their aging.
These are the parts of eukaryotic cells present in animals and the functions of each one; We hope that the information has been easy to understand and any questions, the comment box is available for your use. We invite you to share the content on your social networks, maybe one of your friends might be interested.
Hello
he served me a lot
helped me a lot
The information helped me a lot. Thank you