In marketing, the product life cycle is part of the tools or support elements, where it allows an evaluation of the products or articles that a company has in the market, that is, this tool refers to when a company evaluates your products once they have been launched on the market.
Performing this assessment is a vital technique for take control of the marketing of a company, since in this way it is possible to obtain relevant figures with which to rely when analyzing the strategies used in the campaigns before and after their launch.
The term was coined by Theodore Levitt (American economist and Harvard professor) in 1965, referring to its exploitation in order to obtain greater benefits. However, after Levitt's initial model, different variations emerged that were published by other professionals in the field, such as Wasson.
How is the product life cycle divided?
Products always go through the same stages or phases, regardless of the market niche that the company covers. Specifically, they are divided into four phases, the first being the introduction, the second referring to crecimiento, going through the maturity and ending in the imminent slope.
However, each product has its own experience in each of the stages; which means that the structure is maintained (as we mentioned). In addition, the period of time also varies according to the article, where some may remain in a phase for longer (or less), for example, a product that lasts more years in the maturity stage, but it generates constant or passive income; while another matures quickly and the decline is just as fast.
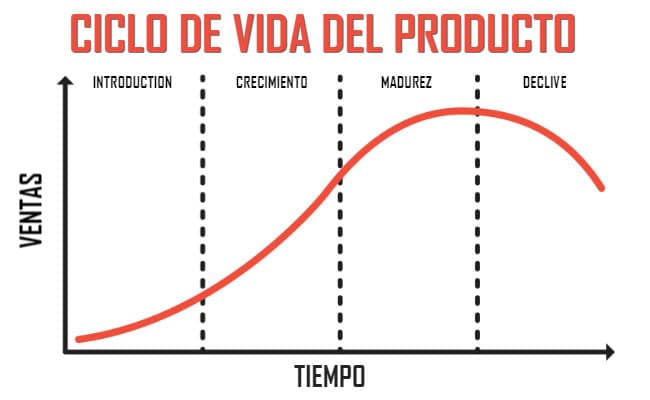
Introductory stage
The introduction refers to when the product is launched on the market for the first time, where it usually has low sales because it is in its initial phase (although there are exceptions) and a investment in marketing campaigns that allow the product to be made known to its target audience, regardless of the size of the niche.
A correct introduction is carried out when previously, the company carried out the corresponding market studies to foresee its behavior. Only in this way will you be able to take into account the essential aspects for the survival of the product.
It is also important to note that since it is a new product with low sales, the marketing costs are usually higher than the benefits. Despite this, it must be invested to promote and publicize it. Only in this way can a balance be achieved that later, if done in the right way, will begin to show greater benefits.
According to studies, due to their low profitability, the vast majority (approximately 70%) of products do not pass the introduction phase, that is, they fail to launch. Therefore, prior research is essential to overcome this stage and begin to perceive the benefits.
Growth phase and turbulence
There are products that go through a period of turbulence, in which they simply collapse from one day to the next, but this does not mean that the business model or niche is no longer profitable (also with many exceptions), but only for a time.
If this is not the case, it would be normal for the product life cycle will go through the growth period, which is reached once one of the most difficult stages (introduction) has been overcome, which allows the development of the product gradually and with it, increasing sales at a higher speed.
At this stage one of the most common characteristics to appreciate are the increases in sales, the arrival of new competitors, similar products with more benefits, the promotion focuses on attracting the product by the brand, among others; which offers the ability to pave the way for product maturity in the market.
Maturity stage
At this stage, the product goes through a period in which normally sales growth begins to slow. However, it is the phase that any company wants to reach with total normality. In addition, this stage usually lasts longer than the others and it is when marketing and advertising techniques can be put into practice, since somewhat difficult challenges are presented.
At this stage, most companies reach a "limit" of production, where it has also been perfected and it seeks to reduce costs in some aspects in order to keep profits balanced.
So basically the product is profitable Although not in an exaggerated way as in growth, but benefits are still being perceived and also, the investment is not so strong, which allows to distribute good dividends.
Another characteristic of the Maturity stage of the product life cycle is the fact that the number of competitors increases, sales prices may decrease due to competition and a great effort must be made to demonstrate to the target audience that the product of the company is better than the others.
Decline phase
Finally, a stage that no company wants to reach is the slopeIn which product sales begin to decline significantly and it is considered the exit from the market, usually due to being obsolete or low profitability due to market saturation.
In this phase the techniques used focus on offering discounts, offers, product redesigns, among others; which will allow you to get rid of the product more easily, because customers often lose the interest that existed at the beginning.
Although most companies do not want to reach this stage, it is practically inevitable for several reasons, which according to Walker, Staton and Etzel are the following:
- There is no need for the product.
- The target audience gets tired of the product.
- A better or lower-priced product is launched on the market.
These are the stages or phases of the product life cycle, which we hope have been detailed enough for the understanding of all our readers. However, we are willing to answer all comments with any questions or concerns about the subject.