If we look around us, we realize, without much effort that everything is constantly changing, nothing in the natural or cultural environment is static, there are changes that occur more gradually than others, but everything, absolutely everything, is constantly changing. evolution.
Of this reality biological species do not escape, which for us, for our understanding, because that is how we have seen them, that is how we have known them and may remain the same during the course of our lives, but those who dedicate themselves to studying them with seriousness and scientific methodology, know that each of the living species that we know and are around us, is the result of a series of transformations and will continue to be so, as long as there is life on earth. Because life is continuous biological evolution.
Now, since the earliest times of mankind there has been speculation about the immense variety of living organisms that exist on earth and it might be asked what mechanisms are responsible for the diversity of forms and functions that different species adopt? Or how do human beings fit into this grand stage of life?
Let's look at history a bit
Most of the initial ideas about the origin of life are related to magic or religion. Some believed that organisms were formed from inert organic matter. Such spontaneous generation theories date back to the time of the Greek philosophers Anaximander and Aristotle. For many it seemed obvious, for example, that the larvae of flies were generated spontaneously from rotten meat. In 1861 the French chemist and bacteriologist Louis Pasteur definitely developed the theory of spontaneous generation.
Through the centuries, religion has had a determining influence on the worldview of societies: believers considered the creation of organisms as an act of their particular God or gods. The Judeo-Christian societies, for example, accepted the truthfulness of the real of creation, as it is written in the genesis of the Old Testament. This belief known as creationism, holds that the different species of living organisms were created by God, in their current form, and that this cannot change. Until about the middle of the XNUMXth century, most scientists approved of this approach, and today many Christians still cling to the literal truth of genesis. However, scientific opinion has changed in light of some remarkable discoveries made by naturalists and geologists throughout the XNUMXth and XNUMXth centuries.
By the 1730s the Swedish naturalist Carolus Linnaeus (Carlvon Linné) in Spanish Linnaeus, had undertaken his innovative task of identifying the affinities between different species by systematically ordering them by groups.
(Taxonomy) this led to a closer look at the similarities that exist between certain species. Anatomical studies began to reveal how very different organisms at first glance may share certain structural characteristics, raising speculation about some kind of kinship or relationship of origin between them.
The geological footprint
Geologists discovered that the rocks contained various layers (strata), formed at different periods. These rock strata dated from long before any date set by the church for the creation of the world.
Some strata contained fossil remains of animals and plants that had lived during the period when the rock was forming: many of these fossils belonged to organisms unknown in the contemporary world. In fossils of successive strata, structural similarities could be distinguished that represented organisms that had lived in successive periods of the past. The older the rocks on which they were found, the simpler and more primitive were the life forms.
All of this suggested that today's organisms came from primitive life forms, which had undergone a process of gradual change, that is, biological evolution.
Theories of evolution
At first it was not so easy for the world to accept the evidence of evolution, despite being palpable. For a long time, the church, without arguments or valid proof to deny, the fact of the fossil record, and proposed that God had placed fossils in the rocks during creation in order to test the faith of the believers.
erasmus darwinBritish physician, philosopher and poet, he was the author of one of the first theories of evolution. erasmus darwin He proposed that life had developed from a single source, and described the importance of the struggle for life and sexual selection as a mechanism for evolutionary change. Many of his ideas influenced his grandson, the naturalist Charles Darwin, whose own theory of evolution made a lasting impact on biology. However, the author of the first truly general theory of evolution is the French naturalist Jean- Baptist de Lamarck.
Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, Knight of Lamarck, was a respected but controversial figure. He is credited with having given the name to the science of "Biology" and was the popular author of the study on the flora of France. He also wrote a seven-volume treatise on "invertebrates," a term he introduced to describe animals without backbones. His interest extended to other fields, including geology and the study of paleontology fossils, and although he initially believed that species remained unchanged in the 1790s he converted to the belief in biological evolution.
Lamarck, became convinced that organisms evolved increasingly complex. He also concluded that the supposedly extinct fossil species had not disappeared, but had simply evolved to more modern forms and that biological evolution was a gradual process. Lamarck contributed to the belief that structures body are strengthened and developed due to its repeated use, and that the little-used parts are weakened or diminished: the hypothesis of use and non-use In a similar way I accept that these characters acquired during the life of organisms can be transmitted to their offspring.
A popular illustration of this fact is the giraffe's long neck. According to the hypothesis of use or non-use, the efforts of the giraffes to reach the leaves of the high branches would cause the stretching of the neck and their offspring would inherit this acquired character and therefore have slightly longer necks. Thus, through time and many generations, a population of long-necked giraffes would have evolved.
Lamarck published his theory of evolution in Zoological Philosophy and it was widely criticized. His name remains linked in a rather unfair way to the discredited notion of inheritance of acquired characters, called lamarquism.
Even Charles Darwin proposed a similar inheritance mechanism, which he called pangenesis. Only the rediscovery, in 1900, of the Mendel's pioneering genetic experiments it would make a more accurate picture of inheritance appear.
It is currently known that the traits inherited from their parents by the offspring are acquired at the time of fertilization, that is, they are transmitted, in the form of genes, by the DNA of the sperm and the egg of the paternal and maternal organisms and this is not it is affected by the later way of life of these organisms. Although DNA can be altered by various types of mutation and by various environmental factors, such as ionizing radiation, it cannot be altered by the way organisms behave.
Darwinism
In 1858, the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace sent Darwin a text entitled on the tendency of varieties to deviate indefinitely from the original type, based on his studies of the fauna of the Malay archipelago, present-day Indonesia. This scientist had observed that these Asian species. They were more advanced in evolutionary terms than the Australians and he suggested that they had evolved after the two continents separated.
Darwin was surprised to find that Wallace was read to the Linnaean society of London, but neither Darwin nor Wallace were present and the occasion aroused little interest.
In November 1859 Darwin published the origin of species through natural selection or the preservation of favored races in the struggle for life. In this book Darwin recognized that Wallace had reached almost exactly the same general conclusions as I about the origin of species.
The Darwinian theory of natural selection is summarized in the following points:
- Variations in shape can be found among individuals of any species, size, color, among others, of many of its characteristics.
- Species that reproduce sexually have many more offspring than are needed to maintain the number of individuals in the population.
- On average, any individual has only a slim chance of surviving to sexual maturity.
- This probability of survival It may be greater if the individual has certain characteristics of size, shape, color, between hours that make him better adapted to his environment. It is then said that he has a selective advantage over his peers.
- Individuals who are better equipped to survive in their environment until sexual maturity will have a better chance of procreating and transmitting favorable characteristics to their offspring.
- Conversely, those individuals whose characteristics make them less likely to survive to sexual maturity will have fewer offspring and less likely to transmit their characteristics.
- After many generations the number of descendants with favorable characteristics will increase and the number and number with less favorable characteristics will decrease.
Darwin's book caused a scandal, and its author was censored as a traditionalist. One of the main objections to Darwin's theory was that it implied the absence of any fundamental difference between humans and "lower" animals, according to Darwin humans were simply more evolved than other primates such as lemurs, monkeys and other apes. At the time, at the time this idea was in contradiction with basic religious principles.
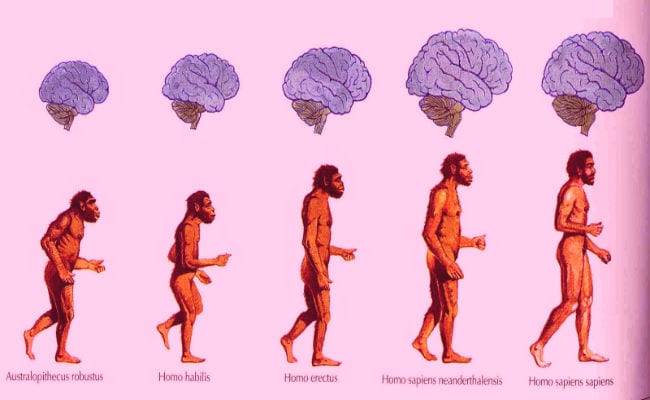
However, Darwin was strongly supported by an important group of scientists of the time. Darwin's ideas prevailed and eventually achieved widespread adaptation. Today it is a widely accepted idea that modern man (homo sapiens) evolved from monkey-like ancestors.
Natural selection
The difficulty in studying selection and natural evolution in the most living species lies in the very gradual nature of the process. However, some characteristics that affect the probability of survival can change rapidly: evolution does not necessarily take thousands of years. For example, species threatened by predators they can evolve relatively quickly, by natural selection, to lessen the threat of capture.
Natural selection is most easily studied in organisms with a short generation time. Bacteria, for example, can have a generation time of only 20 minutes, so that natural selection can produce important changes in these organisms in a relatively short period of time.
Modern theory
The modern version of Darwin's theory, Neo-Darwinism, also known as modern synthesis or synthetic theory, integrates XNUMXth century knowledge in genetics and related fields with Darwin's original ideas. Investigations on how genes behave in populations of organisms and current studies on evolution have reaffirmed the importance of natural selection. In Paleontology, this synthetic approach has provided information on the rhythms of biological evolution over geological time.