Blood is a renewable tissue that is part of organisms, and the cells that are part of this tissue are produced in the bone marrow continuously. As we all know, blood fulfills vital functions in organisms of multiple species, such as defense against infection, gas exchanges, and nutrient distribution.
Did you know that blood is made up of a set of cells in colloidal solution? Yes, blood contains a cellular composition made up mostly of white and red blood cells, suspended in a liquid and nutritious medium. This liquid medium is known as blood plasma.
Although we generally think of the concept in a global way without considering its components separately, the truth is that plasma itself constitutes an element that fulfills multiple functions of relevance for the functioning of the organism.
Definition of plasma as a blood component
Blood plasma is a fluid of a salty nature, yellowish or amber color, translucent in color, in which elements called "forms" are immersed, which constitute the cellular part of the blood. It is not only the liquid fraction of this vital fluid, it is also the most abundant, since it constitutes 55% of the total volume of the blood.
The main function of this component is to transport nutrients and waste from vital processes.
Composition of blood plasma: It is constituted in an aqueous solution, of colloidal character, constituted by 91% of water, and solids suspended in it. It has been determined that it has a density similar to that of water, although it is slightly higher, since the solids present, such as proteins, influence the viscosity.
The largest dissolved component is made up of proteins (8%), among which we can name:
- Globulins: They are synthesized in the liver and constitute antibodies against infectious diseases.
- Fibrinogen: Playing an important role in coagulation, this protein is an important part of the composition of plasma.
- Albumins: They represent 60% of the plasma proteins, as the previous ones originate in the liver, and their role is to carry out the transport of lipids and steroid hormones. They are also attributed responsibility in processes such as oncotic pressure, which is of vital importance in maintaining the balance in fluids that irrigate the organs.
- Lipoproteins. They have a buffering effect, buffering pH changes in the blood.
It is also important to mention those components that constitute a lower proportion (traces), of just 1% of the total composition of the plasma, however it is important to be aware of them: carbohydrates, lipids, hormones, enzymes, urea, sodium, potassium and carbonates.
Plasma extraction
It is common to confuse blood plasma with a liquid of different constitution called serum, since both come from the blood flow, however, the fundamental difference between the two is the composition, since plasma is the liquid part of the blood without clotting, for Therefore, it has a more nutritious constitution, whereas serum is the liquid part of clotted blood, thus lacking components such as fibrinogen.
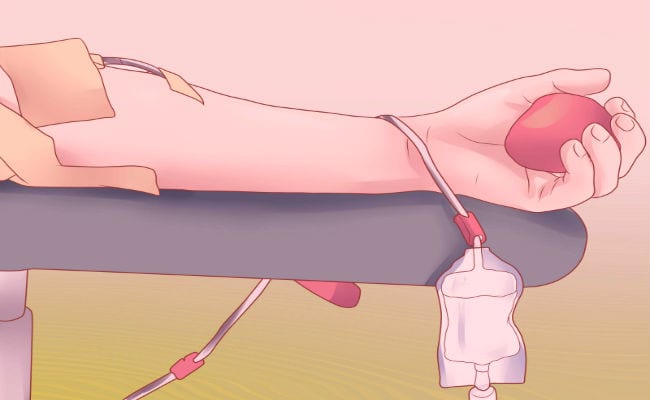
When blood is drawn from the blood vessels, it remains for a short time in a liquid state; To prevent clotting from occurring, it is common to resort to the addition of anticoagulant substances such as heparin, sodium citrate, and ethyldiaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). Subsequently, the non-clotted blood is centrifuged using the Wintrobe tubes, in which the cells settle to the bottom of the tube.
As a product of this process, we observed three differentiated phases in the tube: one with a lower density amber color (plasma) located at the top, in the center we found a small whitish phase made up of platelets, and at the bottom, the cell phase that is more dense reddish in color.
Uses of plasma
In various sectors of medicine, scientists have taken advantage of the generative properties of plasma for the treatment of skin conditions, its action as a clotting agent has also allowed the development of therapies for patients with hematological deficiencies, which has allowed them to improve their quality of life, since they can carry out their daily activities normally.
Biotherapies: These therapies are based on the use of blood plasma in the treatment of coagulation disorders such as hemophilia and primary immunodeficiencies. Its use has also been extended to the treatment of neurological disorders.
Aesthetic procedure: The plasma in the skin stimulates the fibroblast, which consists of a component that promotes its elasticity, being the main component of the skin, which increases the production of hyaluronic acid, elastin and collagen, which delay aging, and this it results in the reduction of wrinkles, sagging, and its use in the treatment of stretch marks has also spread. It can also be applied preventively, in the case of younger skin, or as regeneration therapy in aging skin.
The application of platelet-rich plasma is a specific procedure, which means that it must be extracted from the patient's blood, this is done to reduce the risk of allergies and rejection of treatment. It is a procedure It is a painless and outpatient procedure; approximately 45 to 60 minutes are required.
This area also includes its use for the treatment of skin injuries caused by burns.
Treatment for knee osteoarthritis: Observing its action in reducing stiffness and regeneration in cartilage, therapies have been developed in which the use of blood plasma has become popular in the treatment of osteoarthritis in the knee, observing that recovery is favored in up to 73% of cases .
Functions of blood plasma
Most of its functions are derived from the action of the proteins contained in this fluid. Their participation in multiple processes of relevance in the organization is detailed below:
In coagulation: Coagulation is essentially a defense mechanism in the body, in which the clot forms a dense, semi-solid mass that blocks broken blood vessels. Plasma is involved in this process, as it provides three essential substances, such as prothrombin, fibrinogen, and calcium ions. During coagulation, prothrombin and calcium ion (Ca ++) form thrombin, which is a protein responsible for converting fibrinogen (in joint action with calcium) into insoluble fibrin filaments, which constitutes a three-dimensional network that traps erythrocytes and leukocytes, originating that dense mass of fibrin and blood cells, called a clot.
Shipping cost: Since it allows the transport of nutrients, gases and wastes produced in metabolic and cellular processes. In general, this transport function is what promotes the exchange of substances between the organs.
Electrochemical function: Plasma proteins are permeable in nature, and therefore are retained in the vascular compartment, and this has a direct influence on osmotic pressure. When these proteins, which are large molecules, do not diffuse through a semipermeable membrane, their presence in this medium alters the distribution of the ionic particles. This property determines its role in electrolyte regulation.
Oncotic pressure: For the maintenance of this type of hydrostatic pressure, the proteins immersed in the plasma exert a direct effect, as mentioned in the previous item, on the osmotic pressure.. And that effect is closely associated with the action of these large molecules on blood vessels. Proteins exert pressure, because the movement of water occurs motivated by a gradient, that is, it is directed from an area of greater potential to one of less, therefore, the water in the human body will always be directed to the place where there is a higher concentration of some dissolved substance.
In the case of the proteins contained in the plasma, it happens that there is a higher concentration in the blood plasma than in the interstitial fluid (which is the one that bathes the cells of the tissues), which makes the water in this fluid tend to enter to regulate the water pressure on both sides of the capillary wall. In this way, a person's plasma volume and total blood volume are maintained.