The cerebellum is located in the dorsal cranial fossa, posterior to the brain stem and inferior to the occipital lobe, it is an odd middle organ that has a size between anteposterior diameter of 5.6-6.6 centimeter and transverse diameter of 8-10 centimeter, with a height of 4-5 centimeter and an approximate weight 130 kg.
Lesions in this area are not usually associated with paralysis, but rather with motor dysfunctions, such as posture, difficulty in executing some movements and learning them.
There have been some studies in animals that have shown that the cerebellum is the main in charge of developing motor skills, such experiments showed that the damage caused in it caused those affected to execute strange and clumsy movements.
Although at present it has been shown that the cerebellum fulfills much more functions than just the motor system, and even more complex such as the development of language, some cognitive processes, attention and artistic abilities.
What is the cerebellum?
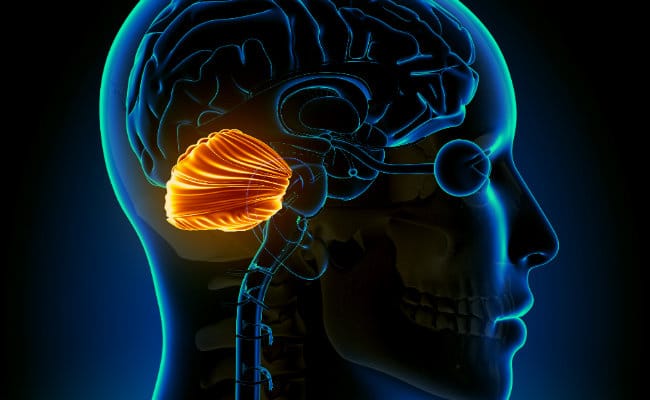
It is the regulator of physiological tremor, called for being a region of the brain that is characterized by integrating all the sensory and motor pathways to the nervous system, this is closely connected with other brain areas and with the spinal cord through diversities of bundles of nerves, this in turn is in charge of specifying all the information that the cerebral cortex sends to the motor apparatus so that it has a good functioning
The cerebellum is one of the parts that make up the central nervous system, and it is the second largest, after the brain of course, it is located in the lower and posterior parts of the skull.
The brain has certain qualities that identify it for being in charge of all complex motor movements and executions, among the most prominent are the following.
Evolution
It has the ability to divide into three parts during the process of its evolution, which have specific functions.
- Posterior lobe: this is characterized by being the most recent part of the evolution of the cerebellum.
- Anterior lobe: This is called the second lobe in the process of its evolution.
- Flocculo-nodular lobe: It is the oldest part of the entire cerebellum, also known to be primitive.
Functions according to their lobes
The cerebellum has three different functions, which vary depending on the lobe it is using.
- It intervenes and regulates: all automatic and voluntary movements, and in turn also has the ability to coordinate all skeletal muscles to have better control of the entire body, this function is characteristic of the posterior lobe.
- Keep: it is able to maintain muscle tone throughout the body, characteristic of the anterior lobe.
- Balances: the flocculo-nodular lobe has the ability to maintain and establish balance in all muscles and the body, achieving full stability.
Anatomy
It gives accommodation to the unconscious nerve pathways, and is made up of two hemispheres, and specifically in the center of these there is a small cavity called Vermis, which has a shape very similar to that of a worm, and It is where the nerve pathways mentioned above end.
Neurons
Incredibly in the cerebellum there are 50% of the total number of neurons in the entire brain, although this is proportionally 10% of the entire size of the brain.
Neurons are the nerve endings in conjunction with their respective processes.
Local
The cerebellum is capable of establishing three types of connections through its cerebellar pendulums, which are cords of it. The types of connections depend on the pendulum that it uses.
- Lower pendulum: it is capable of interconnecting the medulla oblongata with the spinal cord.
- Middle pendulum: the annular protuberance connects with the neo-cerebellum, these are characterized by being the thickest cords of the three types.
- Upper pendulum: It has the ability to connect the central nuclei of the cerebellum with the brain stem through motor fibers.
Internal configuration
The configurations that the cerebellum possesses are divided into two types of substances according to their color, which are gray and white.
The gray matter is divided into 4 cerebellar nuclei and their cortex, which each have their function, and are as follows.
- Serrated core: this is the one that connects with the neo-cerebellum, and in turn is the most developed.
- Emboliform nucleus: This is the main one in charge of the limbs having their respective motor functionality.
- Globose core: It is characterized by having a shape similar to the letter "S"
- Fastigial nucleus: It is in charge of establishing balance in the body and its muscles.
Appearance
The cerebellum is fully covered by a cerebrospinal fluid, and has a curious ovoid shape, the brain of a man can weigh 9 grams than that of a woman, and can weigh between 150 and 180 grams, in turn, it is composed of three faces: the lower, upper and anterior .
- The lower face: It is directly connected to the occipital fossa of the skull, called the cerebellar fossae, which is supported by the dura mater.
- The upper face: It connects with a wall called the cerebellum tent, and is characterized by having a shape similar to that of a roof.
- The anterior face: the annular pons and the medulla oblongata are connected thanks to this.
Functions of the cerebellum
The main function of this is to coordinate and send the sensory stimuli of movement and sensation, this is the main responsible for reacting to the thousands of possibilities that may exist outside, being able to activate a defense system, flight among others before those mentioned.
Has the ability to perceive and store information coming from the cerebral cortex, to be able to react to any stimulus that the body may have, generating the movements of the muscles, which include skills such as languages, artistic skills such as music, physical skills, among others.
The cerebellum is a part of the brain of many living beings although in some it develops more than in others, as is the case of fish, birds and amphibians, and those that have it more developed can be understood within mammals, being primates the first.
Some pathologies related to the cerebellum
This can present certain failures, caused by injuries, which can lead to serious complications in the motor and linguistic functions of the person who suffers from these pathologies, among the most important are the following.
- Ataxia: It is characterized by presenting difficulty in the voluntary and involuntary movements of the individuals, which generate the appearance of disorders such as hyperthermia, dyschronometry, adiadochcosinecia and asynergia.
- Hypotonia: patients with this pathology may show a decrease in muscle mobility and muscle palpation.
- Involuntary tremor: There is a failure in the cerebellum, which acts as a regulator of body vibrations, so a vibration can be noticed when trying to mobilize any muscle, which is an involuntary movement of the person, so it is not done with intention .
There are also some syndromes related to the cerebellum, which arise as it is injured, damaging or severely affecting people's motor functions, among the most common are the following.
Hemispheric cerebellar syndrome
The main cause of this is an ischemia or tumor found in the cerebellar hemispheres, which present motor difficulties in the extremities, focusing mainly on the legs and arms.
Vermis cerebellar syndrome
It focuses on the lack of control of the central parts of the body such as the trunk and head, preventing the person from keeping them stable, sometimes losing balance, being able to deliberately fall forward or backward.
There are many ways to damage the cerebellum and thus affect the abilities of the body's motor system, such as bruises, poisonings, tumors, infections, trauma, degeneration, vascular problems, and malformations.