In the diversity of the fauna, there are many species that have different survival methods, the same evolution has made each of them adapt to the environment where they live, marine animals for example, have a totally different life from terrestrial animals .
The method of feeding, reproduction and even respiration are some factors that determine the evolution of the animal. Gill respiration, for example, is something of sum importance for fish development and other aquatic animals, because of this, we wanted to give you all the information you need and deserve to know about the respiratory system of fish and other marine animals that breathe through their gills.
What are gills?
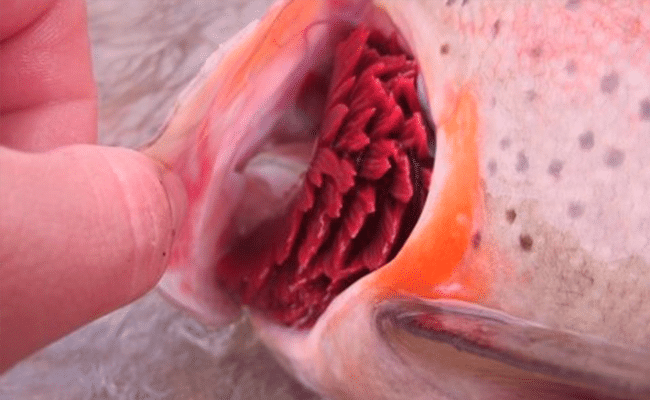
They are external organs that allow fish and some marine animals to do the process of absorption of oxygen from water. We understand that the chemical composition of water is H2O, therefore, the gill is capable of extracting the O2 of water and thus take it to the other organs of the animal's body so that it expels it as CO2 in the middle.
Animals that have this organ in their body are capable of delivering the oxygen that it absorbs to the other body organs to avoid any intoxication. Cellular respiration is done through the gill respiration of the animal and the mitochondria, which is a cellular organelle.
Characteristics of the gills
- Unlike the lungs, the gills are external organs.
- They are appropriate for the constant movement that the animal develops in the water.
- They have two forms, one similar to that of an appendix that is attached to the animal, this type of gill is found in mollusks, larvae, salamanders and newts.
- Its other form is the one usually seen in fish, which are organized within the structures of the animal's pharynx.
- They are related to the circulatory system of the animal.
Types of gills
Thanks to the evolution of the species, we can find marine animals with two types of gills: internal and external. According to the needs of each aquatic species, their ancestors developed a specific gill.
For example, mollusks and newts have a gill similar to an appendage that is found externally to make the animal oxygenation processes a much simpler task for your breathing capacity. The function of the protection of these gills is based on being able to make the oxygenation process much easier for the cells of the animal.
On the other hand, the internal gills are what we commonly see in sharks or other species of small fish. These gills are attached to the body on the outside so that the fish does not have any difficulty moving through the water and in turn does not have oxygenation problems.
External gills
This type of gill is composed of large appendage-shaped sheets that are on the outside of the animal.
According to different evolutionary theories, external gills are the oldest in the marine world.
La external gill It can put the animal's life at risk since it makes it more visible to the predator, there is also a greater possibility that the animal will be injured since they are exposed to touching all the places that it travels.
Invertebrate animals are those that have this type of gill; It has also been proven that these embryonic structures disappear in the larvae, unlike the internal gills that remain in the animal until its metamorphosis or evolution.
Internal gills
For its part, the internal gills are what we usually see in most marine animals such as fish and sharks. According to evolutionary theories, this type of gill is the youngest in evolution.
For millions of years, aquatic animals had external gills, they were in themselves the most common.
After the species diversified, the internal gills were implemented within the organisms of each animal; all thanks to the different nutritional and survival needs that the animal had.
This respiratory system it is much more complex than that of the external gill, since it is located below the pharynx of the fish.
Each of the slits is lined by blood vessels, thus, the oxygen that enters through the gill can travel through the entire circulatory system of the animal, oxygenating the other organs that compose it.
Vertebrates are those that have this type of gills, which despite being the most complex respiratory system, since it is the one that allows the animal to move through the water the most dynamism.
What is branchial respiration and how does it work?

Gill respiration consists of the exchange of gases and oxygen that occurs through the gills.
Just as man breathes through the lungs and air, the being that owns gills need to absorb ocean water, sea, river, lake and other hydrographic scenarios to be able to use the oxygen that makes up the water and thus keep its internal organs and its own species alive.
The gill blades or gills are located on the head of the animal, just at the back.
For the gill respiration process to be fulfilled, it is necessary for the marine animal to absorb oxygen from the water, there are several ways to do it, either by the sea current that surrounds it or with the help of an organ called an operculum.
The oxygen that the animal absorbs is sent to the animal's blood or, failing that, to another fluid that fulfills the same function as blood called hemolymph. Once the oxygen makes this journey, the gas performs cellular respiration thanks to the mitochondria.
Once oxygen has performed its function within the animal's body, it is expelled as carbon dioxide into the water. It is necessary for this gas to be eliminated from the animal's body to avoid poisoning.
Gill-breathing animals
- Frogs
- Octopus
- Clam
- Shark
- Octopus
- Stingray
- Sea hare
- Tent
- Larvae
- Newts
Marine species must be cared for by human beings, each one has a reason for being and for existing; If there is no diversity in the world's fauna, the same evolutionary processes of man can be affected.
That is why we must be aware of the waste that is thrown into the sea, stop doing this type of irresponsibility, it ensures that the life of the different marine species is lasting over time.