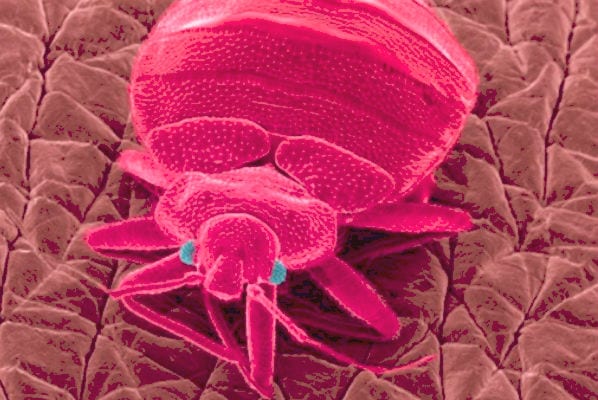
Before knowing the parts that a microscope is composed of, it is important that we know what this object is and where it comes from, which came to revolutionize biological studies in humanity, understanding, in principle, that this is an instrument that allows us to observe elements. or organisms that are too small, which
A Little History
The invention of the microscope remains uncertain. However, despite the mention of a Dutch merchant named Anton Van Leeuwenhoek, who is known as the father of microbiology, Due to his discovery of red blood cells and the improvement of microscopes, the first invention actually came from the hands of an eyeglass manufacturer of Dutch origin, called Zaccharias Janssen and his father Hans Janssen.
This happened around the year 1590. It was a compound microscope that had a tube 45 cm long and 5 cm in diameter with a convex lens at each end. Around 1673 the Dutchman Antoni Van Leeuvenhoek, who was a fabric seller without studies, took an interest in tiny representations of life, which led him to make his own simple microscopes and thus become a microbe hunting scientist.
Some say that he made more than 500 lenses with his own hands, with which they could increase the original size of microorganisms up to 500 times. Van Leeuwenhoek is credited with the discoveries of bacteria, protozoa and according to some publications also sperm.
Microscope classification
There is a wide range of microscopes which classifies them according to several key elements.
- According to the number of lenses: Simple and Composite.
- According to the lighting system: Optical, Electronic, UV light, Polarized light, Fluorescence
- According to the light transmission: Of transmitted light, Of reflected light
- According to the number of eyepieces: Monocular, Binocular, Trinocular
- According to the configuration of elements: Digital, Stereoscopic
There are also other types of microscopes such as: dark field, confocal and phase contrast.
Parts of a microscope
To determine the parts of a microscope we speak of two systems: the mechanical system and the optical system.
As to Mechanic system, also called frame, it is of variable shape and dimension. There are large, medium and small or portable models. Where the greats have to their credit all the elements to guarantee a professional job, as well as allow the exchange of parts and accessories to carry out the most varied jobs.
Despite their size, they have similar characteristics and parts where the structural elements keep the samples to be studied correctly aligned and provide stability to the apparatus. These parts are:
-
Base or foot:
Normally it is the piece that weighs the most to be able to provide the necessary balance and stability essential at the time of the study. It is located at the bottom of the microscope and the rest of the elements are mounted on it. It includes some rubber stops at the bottom to prevent the microscope from sliding on the surface where it is located.
-
Arm:
It is the intermediate piece of the microscope that connects all its parts and constitutes the skeleton of the microscope. It is in charge of connecting the surface where the sample is placed with the eyepiece where it can be observed. The different lenses found in the microscope are linked to the arm, both the objective and the eyepiece
-
Platen:
The sample to be observed is placed there. The vertical position of this surface in relation to objective lenses it is adjustable through two screws that are very close to the base. The stage has a hole in the center through which the sample is illuminated. There are also two clamps attached to this one.
-
Tweezers:
They are fixed on the stage and allow the sample to be held in a fixed position.
-
Coarse screw:
Its function is to adjust the vertical position of the sample with respect to the objective. It is used to obtain a first approach that is then complemented with the next screw called micrometric.
-
Micrometer screw:
It has more precision so it is used to achieve a more exact focus of the sample. Its adjustment must be made slowly for the vertical movement of the platen.
-
Stir:
It is the rotating part where the objectives are mounted. It is worth mentioning that each objective has specific characteristics, that is, each one gives a different increase. And it is through the revolver that the most appropriate one can be selected according to what is merited at the time of the study. Usually the revolver allows you to choose between three or four different objectives.
-
Tube:
As its name implies, it is a tube attached to the telescope arm that allows the connection between the eyepiece and the objectives. It is a structural part that is an essential part in order to maintain the correct alignment of the optical elements.
We have already explained the elements that make up the mechanical system of a microscope. Now we will know the parts of the optical system. This system is in charge of generating the adequate light that is required according to the study to be carried out.
Optical system parts
-
Spotlight or light source:
It is of course an essential element since it is what generates the light that is directed towards the sample. Depending on the type of microscope, the beam of light emitted by the spotlight is directed towards a mirror that at its time diverts it to the sample. The position of the focus will depend on whether it is a reflected light or a transmitted light microscope.
-
Condenser:
It is in charge of concentrating the light rays that come from the focus to the sample. Normally these are divergent so the capacitor changes their direction, leading them to be parallel or even convergent.
-
Diaphragm:
This piece allows to regulate the amount of light that enters the sample. With this action of regulating the light, the option is opened to vary the contrast with which the sample is observed. The diaphragm is located just below the stage and its optimal point depends on the type of sample observed as well as its transparency.
-
Objective:
This element is the set of lenses that are closest to the sample, which produce the first magnification stage. The objectives are mounted on the revolver, thus allowing the selection of the appropriate objective for the required magnification. They have written on the side the increase and the numerical opening that they admit. By nature its focal length is very short.
-
Eyepiece:
After the objective provides the first stage of magnification, the eyepiece being an optical element is the one that provides the second stage of image enlargement. That is, it also enlarges the image that has been previously magnified by the objective, although the magnification provided by the eyepiece is less than that of the objective, it is through this that it is possible to actually observe the sample. This is where the classification of monocular, binocular and even trinocular microscopes occurs. Understanding then that the total magnification of the microscope is given by the combination of the objective and the eyepiece.
-
Optical prism:
According to some medical texts, some microscopes include prisms capable of correcting the direction of light. An essential element in the case of binocular microscopes, since the prism divides the beam of light that comes from the objective and is thus directed towards two different eyepieces.
With all the above described, we can be certain of the elements that are part of a microscope, which is an essential instrument for the study of microorganisms influencing the development of humanity and in the research of enfermedades As well as its possible cures, which are practically invisible to the human eye, it became an essential object for scientific practices. The microscope was established as one of the most important advances in science and one that revolutionized the way the world was viewed.